Carts, Checkout, Orders Introduction
A cart contains a list of the products that a shopper adds to the cart while browsing your catalog. In the context of a cart, a selected product is called a cart item.
A cart item identifies the product, the product price, the quantity selected, and the total price for the quantity selected. The cart displays a running total of the cost for the selected products plus the calculated tax.
You can allow your shoppers to add custom text to a product when adding an item to their carts. This is useful, for example, if you have a product like a T-shirt that can be personalized. See Add product to cart.
After a shopper checks out, the cart is converted to an order, and you can manually delete the cart. If you donʼt delete the cart, it is purged automatically after seven days.
The preview cart feature allows you to set a future date for your shopping cart and view the promotions that will be available during that time period. This feature enables you to validate your promotion settings and observe how they will be applied in the cart. See Create a Preview Cart.
The following diagram shows a typical cart workflow:
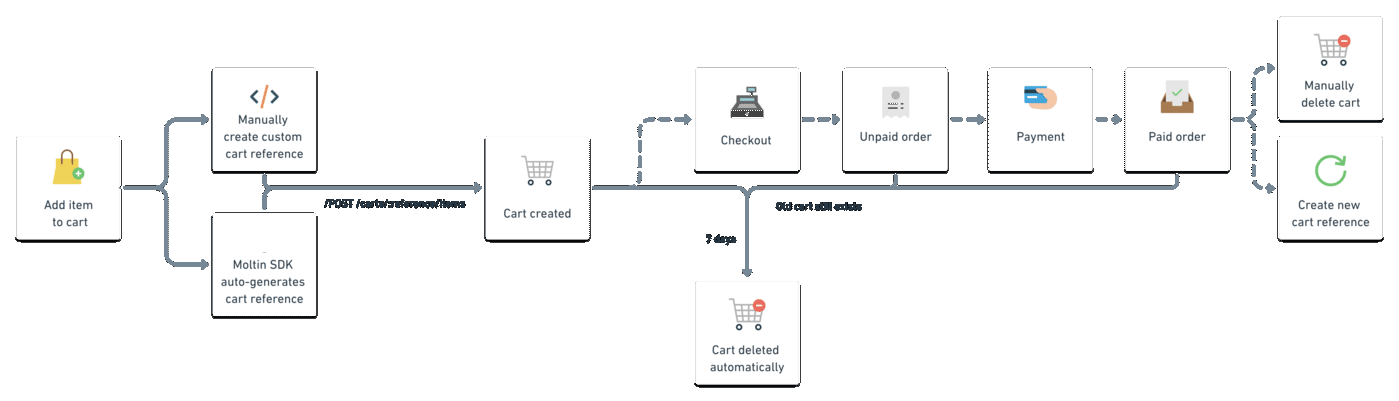
Multiple Carts
Buyers often make purchases based on jobs that they need to perform or outcomes they need to achieve and therefore require more than one shopping cart. For example, a corporate buyer places orders for multiple locations. Each location has a different frequency of ordering and require different products. The buyer can create one cart per location, fill the carts, and then check out the carts quickly. Similarly, shoppers can also create multiple carts for the ease of managing various shopping experiences, such as birthdays or holidays.
Each cart is discrete and separate. Any updates or changes to one cart has no effect on the other carts. A cart persists, that is, it stays with the buyer or shopper even after they use the cart in a checkout. Carts remain available after a checkout.
Authentication
- HTTP: Bearer Auth
| Security Scheme Type: | http |
|---|---|
| HTTP Authorization Scheme: | bearer |